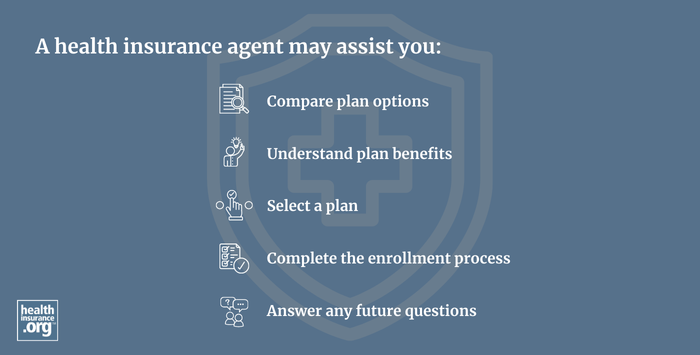
What is a health insurance agent?
An agent is an insurance professional who represents one or more health insurance companies and presents their products to consumers. An agent must be licensed as an insurance producer by each state where they sell coverage. An agent must pass an exam to get licensed, and complete ongoing continuing education in order to keep their license(s) active. If they work with a health insurance Marketplace/exchange, they must also be certified by the exchange and complete the exchange's annual training process.
Many agents are independent and represent more than one carrier (and are sometimes referred to as brokers,1 although the two terms are not necessarily interchangeable2). But some agents are captive, which means that they work exclusively with one carrier and won’t offer another carrier’s plans and products.
Some insurance companies only use captive agents to sell their products. But this is fairly uncommon in the individual major medical market now that the Affordable Care Act has been implemented and most agents/brokers help people select from among a variety of plans available in each state's exchange.
Agents are paid a commission by the insurance companies they represent. For each enrollee that the agent has with a given insurance company, the insurer will pay the agent a commission. For products sold in the individual and small-group health insurance market, premium rates must be filed with the state insurance commissioner before the start of the plan year, and broker commissions are incorporated into those rates as an administrative expense. So the amount that an insurer charges for an individual or small group policy will not vary depending on whether an agent assists with the enrollment.3
Footnotes
- “Insurance Brokers and the ACA: Early Barriers and Options for Expanding Their Role” Urban Institute, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. Feb. 2015 ⤶
- “Insurance Agents vs. Insurance Brokers vs. Insurance Producers” Agent Sync. Feb. 28, 2025 ⤶
- “CCIIO Technical Guidance (CCIIO 2015—0001): Questions and Answers Regarding the Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) Reporting and Rebate Requirements” Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. May 27, 2015 ⤶
