What is fee-for-service?
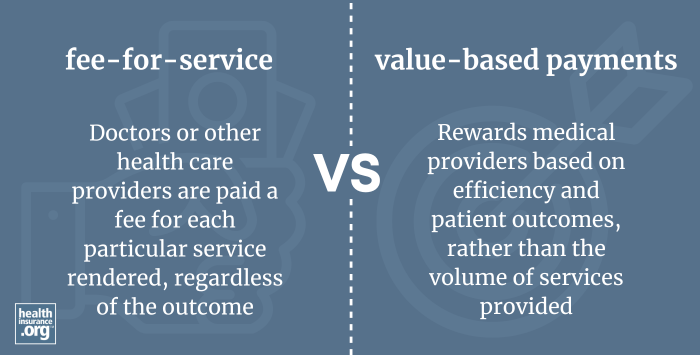
Fee-for-service is a system of health insurance payment in which a doctor or other health care provider is paid a fee for each particular service rendered, regardless of the outcome.
This is in contrast to alternative models, including bundled payment, patient-centered medical homes, value-based care, and accountable care organizations.
There has been a shift in the last several years away from fee-for-service payment models and towards value-based payments that reward medical providers based on efficiency and patient outcomes, rather than the volume of services provided.
In the Medicaid program, nearly three-quarters of all enrollees were enrolled in some type of comprehensive managed care program (managed by a private insurer) in 2021, while just over a quarter were enrolled in fee-for-service Medicaid in which the state paid their medical providers directly for the care they received.1
In the Medicare program, Original Medicare operates on a fee-for-service basis (as opposed to Medicare Advantage, which is administered by private insurers that operate managed care programs). But about a third of all Original Medicare beneficiaries were enrolled in accountable care organizations as of 2023.23 Their medical providers are still paid on a fee-for-service basis, but they can earn more by providing quality care in a cost-efficient manner.
Footnotes
- "Exhibit 30. Percentage of Medicaid Enrollees in Managed Care by State and Eligibility Group, FY 2021" MACPAC.gov. Feb. 2023 ⤶
- "Shared Savings Program Fast Facts – As of January 1, 2023" CMS.gov. Jan. 1, 2023 ⤶
- "Medicare Monthly Enrollment — January 2023" CMS.gov. Accessed Oct. 1, 2024 ⤶
